Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
- Living organisms require energy to perform and maintain life processes such as movement, nutrition and excretion
- This energy is released by the process of cell respiration
- Energy released during the reactions of respiration is transferred to the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
- The energy is transferred in a series of small steps
- Heat is lost at each step, which is used to regulate body temperature in endotherms
- ATP is a small and soluble molecule that provides a short-term store of chemical energy that cells can use to do work
- Its solubility and size enables it to move easily in cells and living organisms by facilitated diffusion
- It is vital in linking energy requiring and energy yielding reactions
- ATP is described as a universal energy currency
- Universal: It is used in all organisms
- Currency: Like money, it can be used for different purposes (reactions) and is reused countless times
- The use of ATP as an ‘energy-currency’ is beneficial for many reasons:
- The hydrolysis of ATP can be carried out quickly and easily wherever energy is required within the cell by the action of just one enzyme, ATPase
- A useful (not too small, not too large) quantity of energy is released from the hydrolysis of one ATP molecule - this is beneficial as it reduces waste but also gives the cell control over what processes occur
- ATP is relatively stable at cellular pH levels
Structure of ATP
- ATP is a phosphorylated nucleotide
- It is made up of:
- Ribose sugar
- Adenine base
- Three phosphate groups
ATP Diagram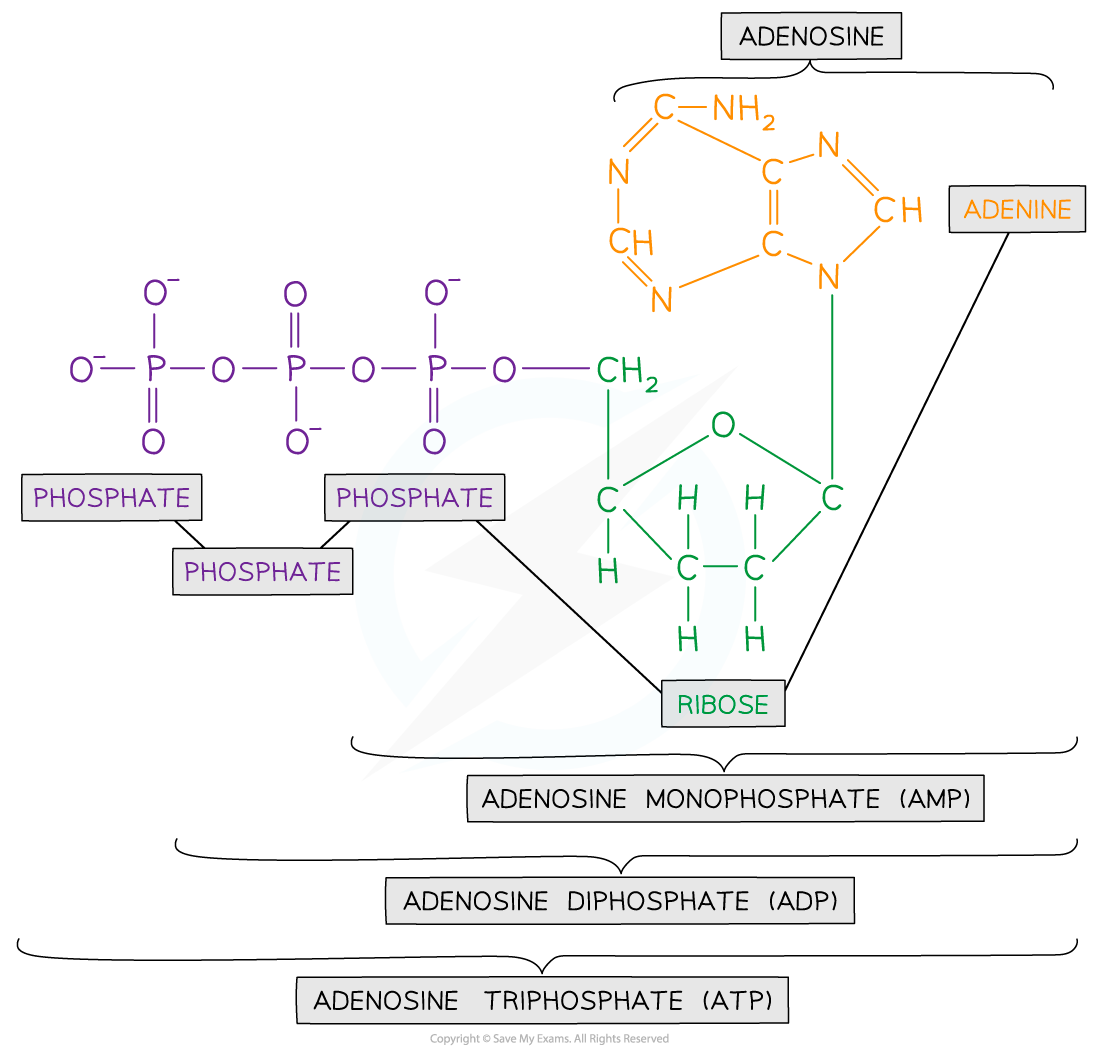
Structure of ATP contains ribose sugar, an adenine base and three phosphate groups
Features of ATP Table
| Feature | Benefit |
| Releases a small but sufficient quantity of energy | This is enough energy to drive important metabolic reactions while keeping energy wastage low |
| Exists as a stable molecule | It doesn't break down unless a catalyst (ATPase) is present so energy won't be wasted |
| Can be recycled | The breakdown of ATP is a reversible reaction, ATP can be reformed from ADP and Pi. This means the same molecule can be reused elsewhere in the cell for different reactions |
| Hydrolysis is quick and easy | Allows cells to respond to a sudden increase in energy demand |
| Soluble and moves easily within cells | Can transport energy to different areas of the cell |
| Forms phosphorylated intermediates | This can make metabolites more reactive and lower the activation energy required for a reaction |
Exam Tip
Be careful not to use the terms energy and ATP interchangeably. Energy is the capacity or power to do work while ATP is a molecule which carries energy to places in the cell that need it in order to do work.




