The endocrine system
- A hormone is a chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland and carried by the blood
- The endocrine glands that produce hormones in animals are known collectively as the endocrine system
- A gland is a group of cells that produces and releases one or more substances (a process known as secretion)
Glands of the endocrine system diagram
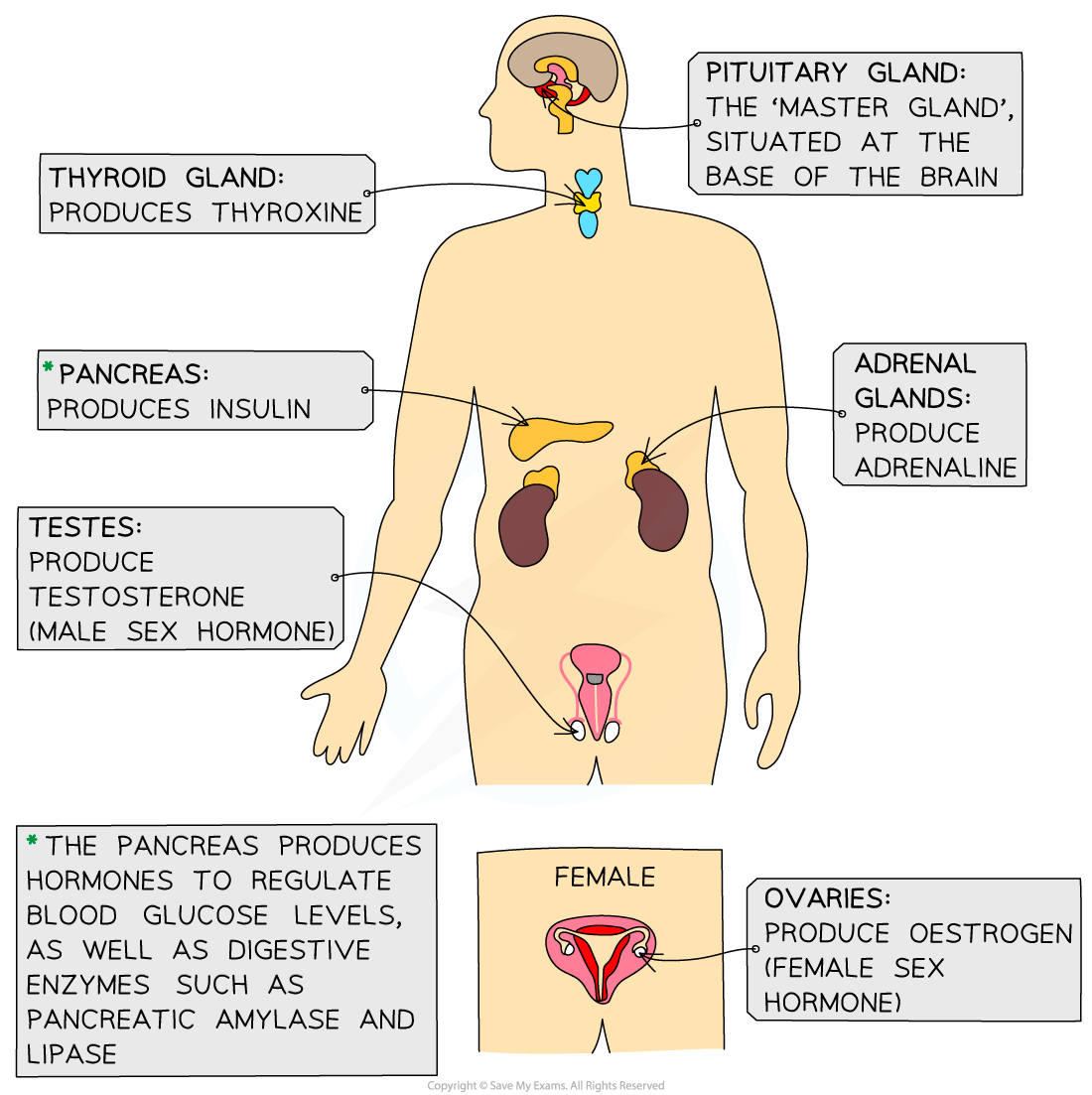
Hormones are produced in the glands and travel round the body in the blood
- Hormones are chemicals which transmit information, via the blood, from one part of the organism to another and that bring about a change
- They alter the activity of one or more specific target organs
- Hormones only affect cells with receptors that the hormone can bind to
- These are either found on the cell surface membrane, or inside cells
- Receptors have to be complementary to hormones for there to be an effect
- Effects can be long lived, as long as hormones are bound to the receptors
- Hormones are used to control functions that do not need instant responses
- They travel more slowly in the blood compared to a nervous impulse




