Diffusion can be studied using visking tubing. Students set up an investigation in which equal volumes of each of the following solutions were placed into separate visking tubings:
0.7 mol dm-3 sodium chloride
0.7 mol dm-3 glucose
The visking tubings, each of the same size, were placed in distilled water and maintained at a constant temperature of 23°C. The volume and mass of the bags were measured at 5 minute intervals for 160 minutes.
The data recorded is shown below.
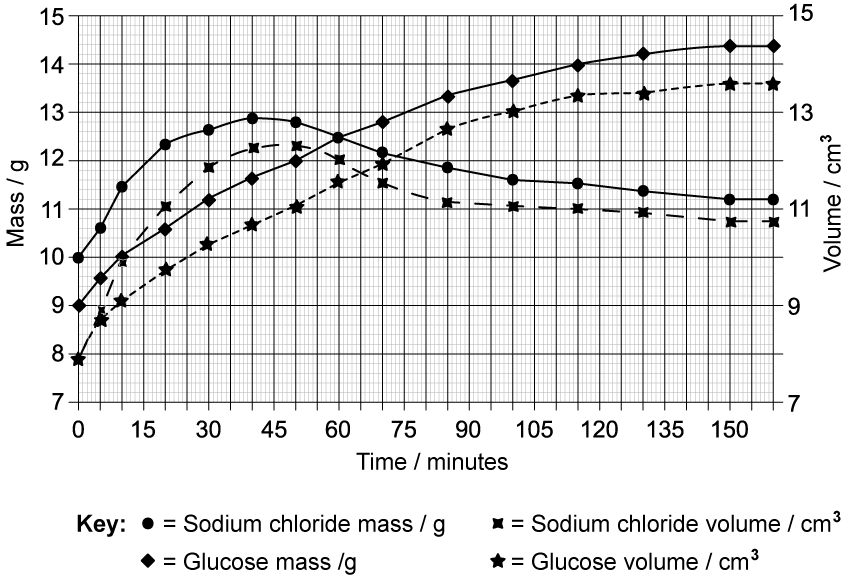
Calculate the rates of increase in mass and in volume for the visking tubing containing glucose solution during the first 30 minutes.












