- Staff appraisal is a process where a manager or supervisor assesses an employee's job performance
Diagram: Discussion Points in Employee Appraisals
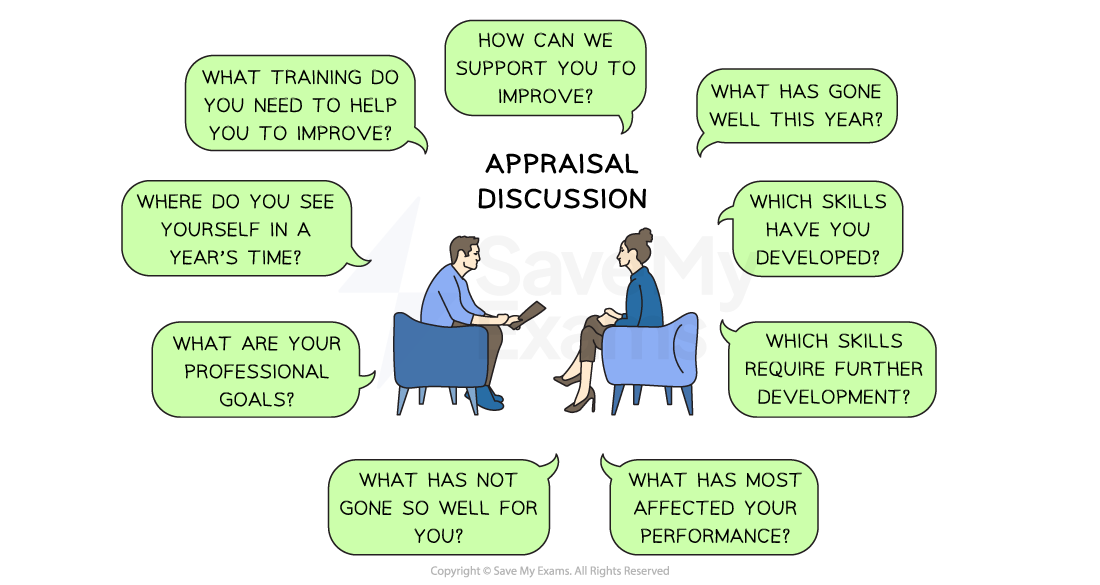
Appraisal discussions reflect on employee performance and establish goals for the future
- Performance is measured against the tasks and responsibilities stated in the employee's job description
- Constructive feedback is given and there is a discussion of goals and development opportunities
Advantages and Disadvantages of Employee Appraisals
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
- Feedback & Communication
- Structured platform for managers to give constructive feedback on employee performance
- Open & honest communication helps to address concerns & set expectations
|
-
Subjectivity
- Can be influenced by personal biases or prejudices of the appraiser
- Managers may evaluate employees differently based on personal relationships or perceptions
|
-
Performance Improvement
- Identifies where employees may need training, development or support to improve performance
- Encourages self-awareness and self-improvement
|
-
Anxiety & Stress
- Employees may fear feedback or potential negative consequences
- High-stakes appraisals can lead to demotivation or performance anxiety
|
-
Recognition & Motivation
- Recognises & rewards employees for their achievements & contributions
- Opportunity to acknowledge employees' hard work & dedication
|
-
Time-Consuming
- Takes both managers and employees away from other productive work
- Filling out forms and conducting meetings can be cumbersome
|
- Decision-Making
- Supports decisions related to promotions, salary increases & bonuses based on merit
- Identifies high-potential employees for leadership development
|
-
Inaccuracies
- May not accurately reflect an employee's performance due to a lack of objectivity
- The process may fail to capture the full range of an employee's contributions and skills
|


