Standard Enthalpy Change
Standard conditions
- To compare the changes in enthalpy between reactions, all thermodynamic measurements are made under standard conditions
- These standard conditions are:
- A pressure of 100 kPa
- A concentration of 1 mol dm-3 for all solutions
- Each substance involved in the reaction is in its standard state (solid, gas or liquid)
- Temperature is not part of the definition of standard state, but a temperature of 298 K (25 oC) is usually given as the specified temperature
- To show that a reaction has been carried out under standard conditions, the symbol ⦵ is used
- Eg. ΔHꝊ = the standard enthalpy change
Standard Enthalpies
- There are a few Standard Enthalpy changes which are used commonly in energy calculations and they are summarised below:
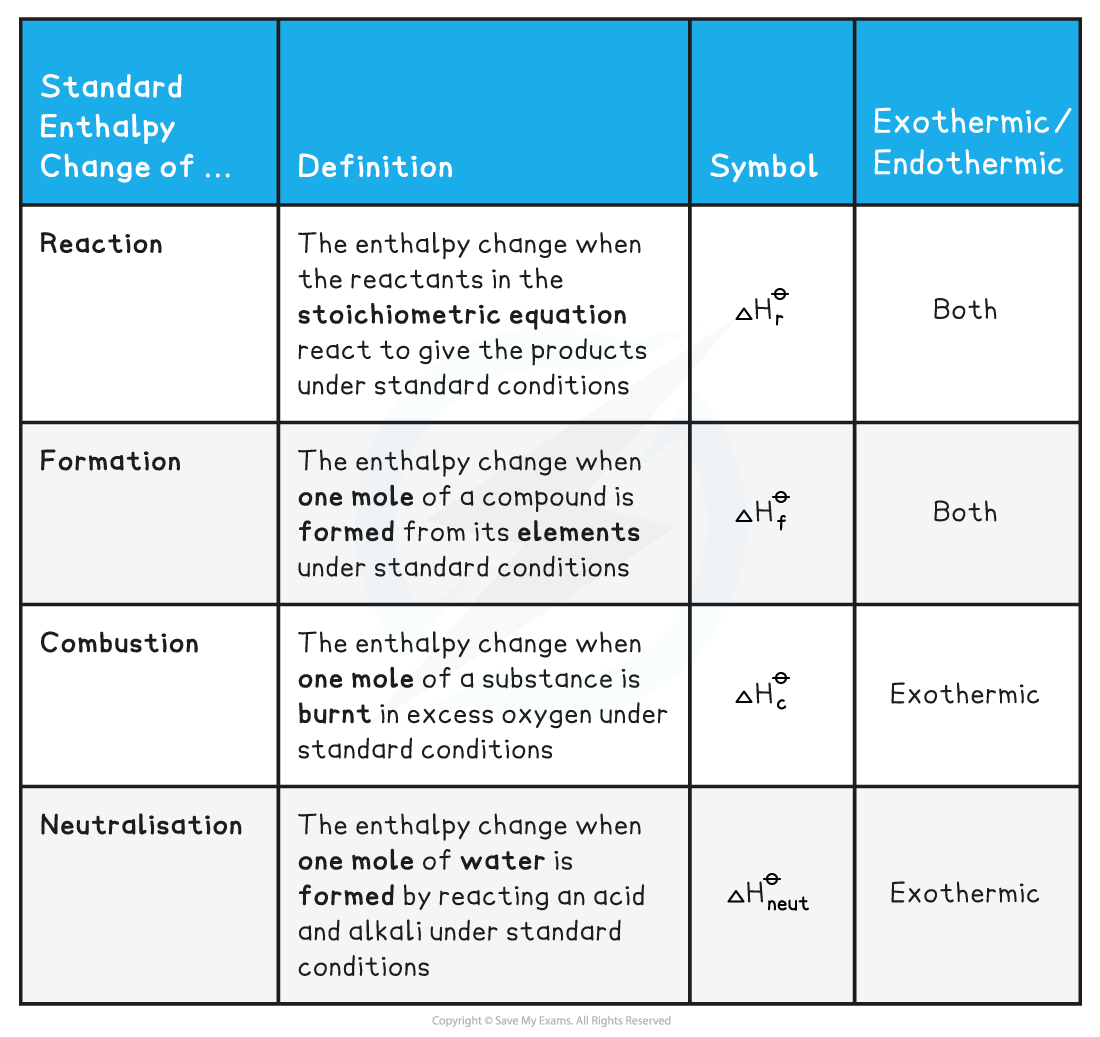
- Practice your understanding of enthalpy changes on the following worked examples:
Worked example
One mole of water is formed from hydrogen and oxygen releasing 286 kJ
H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) → H2O (l) ΔHrꝊ= -286 kJ mol-1
Calculate ΔHr for the reaction below:
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) → 2H2O (l)
Answer:
- Since two moles of water molecules are formed in the question above, the energy released is simply:
ΔHr = 2 mol x (-286 kJ mol-1)
= - 572 kJ
Worked example
Calculate ΔHr for the reaction below
4Fe (s) +O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s)
given that ΔHf Ꝋ [Fe2O3 (s)] = - 824 kJ mol-1Answer:
- Since two moles of Fe2O3 (s) are formed the total change in enthalpy for the reaction above is:
ΔHf = 2 mol x ( -824 kJ mol-1)
= - 1648 kJ
Worked example
Identify each of the following as ΔHrꝊ, ΔHfꝊ, ΔHcꝊ or ΔHꝊneut
- MgCO3 (s) → MgO (s) + CO2 (g)
- C (graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g)
- HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Answer:
Answer 1: ΔHrꝊ
Answer 2: ΔHfꝊ as one mole of CO2 is formed from its elements in standard state and ΔHcꝊ as one mole of carbon is burnt in oxygen
Answer 3: ΔHneutꝊ as one mole of water is formed from the reaction of an acid and alkali
Exam Tip
You need to learn well the Standard Enthalpy change definitions as they are frequently tested in exam papers

