Calorimetry
Measuring enthalpy changes
- Calorimetry is a technique used to measure changes in enthalpy of chemical reactions
- A calorimeter can be made up of a polystyrene drinking cup, a vacuum flask or metal can
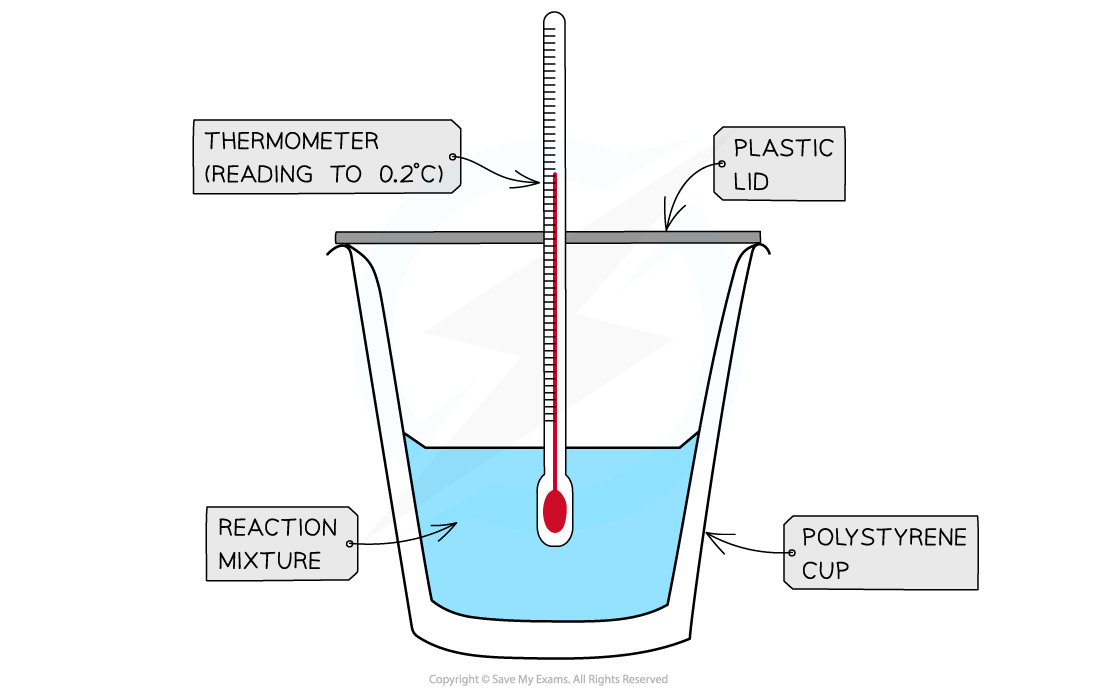
A polystyrene cup can act as a calorimeter to find enthalpy changes in a chemical reaction
- The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 K is called the specific heat capacity (c) of the liquid
- The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1
- The energy transferred as heat can be calculated by:

Equation for calculating energy transferred in a calorimeter
Worked example
The energy from 0.01 mol of propan-1-ol was used to heat up 250 g of water. The temperature of the water rose from 298K to 310K (the specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J g-1 K-1.Calculate the enthalpy of combustion.
Answer:
Step 1: q = m x c x ΔT
m (of water) = 250 g
c (of water) = 4.18 J g-1 K-1
ΔT (of water) = 310 - 298 K
= 12 K
Step 2: q = 250 x 4.18 x 12
= 12 540 J
Step 3: This is the energy released by 0.01 mol of propan-1-ol
Total energy ΔH = q ÷ n = 12 540 J ÷ 0.01 mol = 1 254 000 J mol-1
Total energy = - 1254 kJ mol-1
Exam Tip
There's no need to convert the temperature units in calorimetry as the change in temperature in oC is equal to the change in temperature in K
